vivado UART串口学习记录
UART串口连线
ps端两个串口UART0和UART1,其中UART0负责与蓝牙模块交互,UART1通过串口助手打印调试信息。
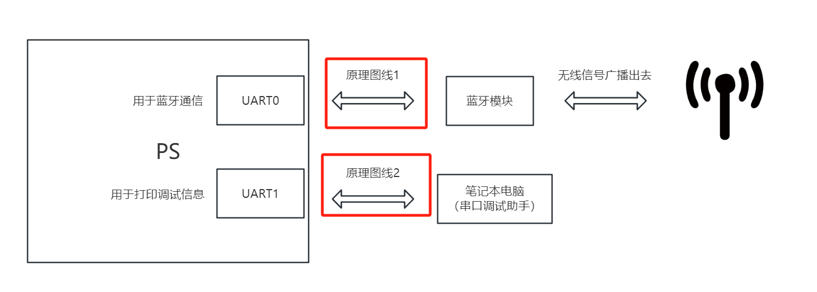
在原理图中,ps端只能找到一个UART串口,这个串口是UART1,和蓝牙连接的UART0使用的是EMIO,连接到了AA25和AB25上面。
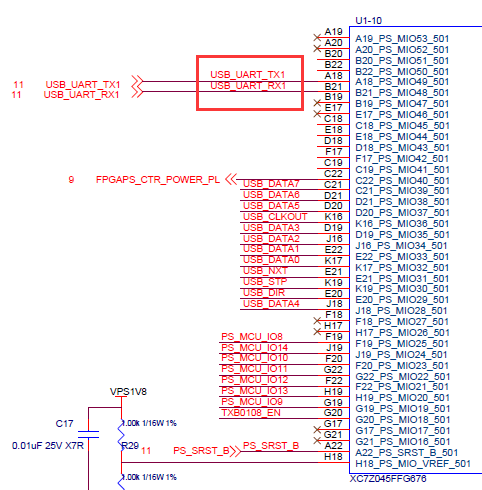
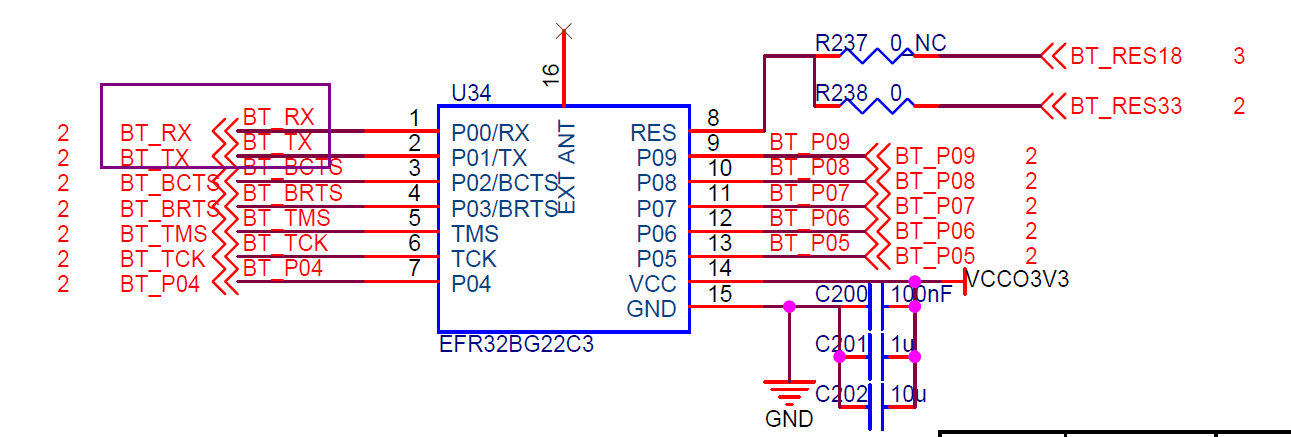
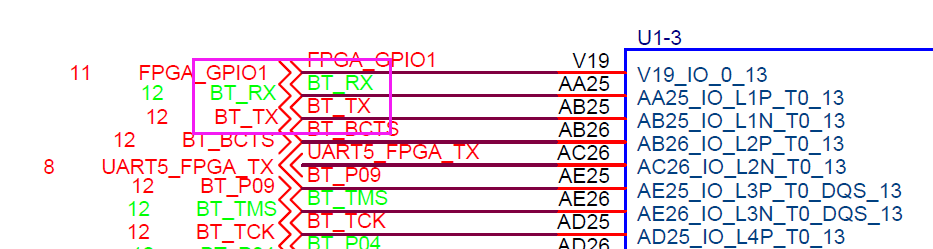
总结一下就是蓝牙的UART0使用EMIO,端口是AA25和AB25,串口助手连接的是MIO,端口是48和49.
具体函数
main函数里面的配置包含了如下几个部分
//------------------------------UART1(printf)-----------------------------
PsUartInit(&psUartPrintInst, UART1_DEVICE_ID);
//------------------------------UART0(BLE)--------------------------------
PsUartInit(&psUartBLEInst, UART0_DEVICE_ID);
// ---------------------------- GPIO -------------------------------------
PsGpioInit(&gpioInst, GPIO_DEVICE_ID);
BLEPinGPIOSet(&gpioInst);
// ---------------------------- GIC --------------------------------------
GicInit(&psGicInst, SCUGIC_DEVICE_ID);
这些函数都包含在驱动里面,PsUartInit()是初始化UART,PsGpioInit()初始化GPIO,这些都是UART和GPIO的常规操作,可以理解为将我们定义的各种实例与对应的设备ID绑定到一起,BLEPinGPIOSet()则是设置蓝牙模块各个引脚的电平情况,具体代码如下。
//***************************************
// Configure Bluetooth related pins
//***************************************
void BLEPinGPIOSet(XGpioPs *InstancePtr)
{
// Setup gpio
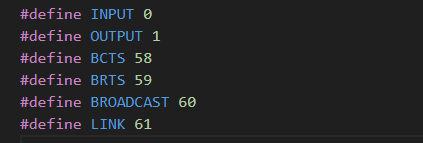
XGpioPs_SetDirectionPin(InstancePtr, BCTS, INPUT); // BCTS,
XGpioPs_SetDirectionPin(InstancePtr, BRTS, OUTPUT); // BRTS,
XGpioPs_SetDirectionPin(InstancePtr, BROADCAST, INPUT); // P04,
XGpioPs_SetDirectionPin(InstancePtr, LINK, INPUT); // P05
XGpioPs_SetOutputEnablePin(InstancePtr, BRTS, 1); // RTS
XGpioPs_WritePin(InstancePtr, BRTS, 0);
}
我们可以看到主要是在设置蓝牙各个引脚的输入输出情况,可以对照蓝牙手册来看,top文件中也需要设置输入输出,也要绑定xdc文件。但是理论上讲,如果在top文件里面设置好了引脚的输入输出,设置好了电平,xdc绑定好了端口,就不需要BLEPinGPIOSet()函数来操作了,但是尚未调试成功。
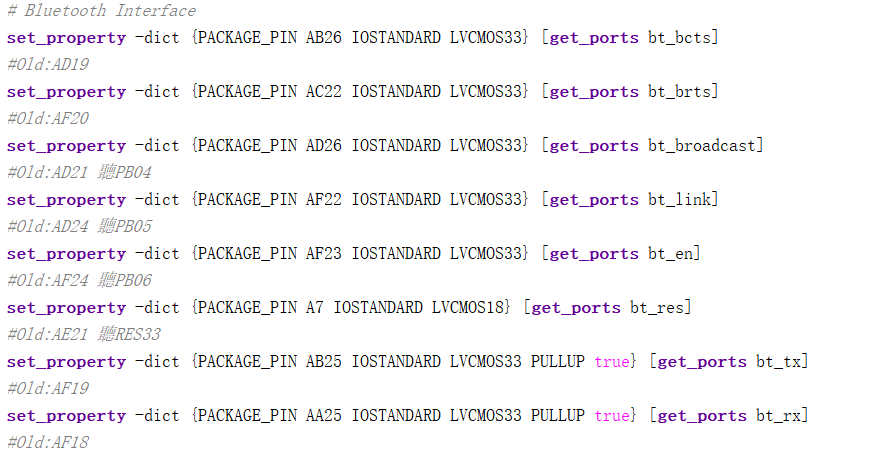
之后就需要我们选择一下测试模块
// Test Mode
// #define UART1Enable(Printf)
// #define UART0Enable(BlueTooth)
要使用哪个模块就将其取消注释,后续的代码有ifdef的条件,有了define之后就会执行相应的代码。例如取消注释掉UART1Enable,以下代码就会生效。
#ifdef UART1Enable
UartISR_init(&psUartPrintInst, &psGicInst, UART1_IRQ_ID);
XScuGic_Enable(&psGicInst, UART1_IRQ_ID);
#endif
UartISR_init()函数代码如下,首先设置了波特率,宏定义的波特率是115200,然后设置工作模式,查阅函数定义可知UART工作模式有四种:Normal, Local Loopback, Remote Loopback, and automatic echo. 这里我们设置的是Normal模式。然后XUartPs_SetRecvTimeout()函数设置接收超时,这里的参数指的是29*4bit时间,也就是说当116bit时间没有接收到数据之后就会超时,这里是根据波特率计算的大约1ms时间。然后使用XUartPs_SetFifoThreshold()函数来设置RX FIFO的阈值,这里设置50,即当FIFO中存储了50字节的数据时产生中断将数据取走,FIFO中最多存储的是64字节。
XScuGic_SetPriorityTriggerType()函数中INTID为中断ID,函数可以理解为,让中断控制器InstancePtrGic来控制INTID的中断,并且设置优先级和触发条件分别为PRIORITY1和TRIG_HIGH_LEVEL. XScuGic_Connect()函数则是将我们要设置的中断与中断服务函数还有回调函数连接起来,使之能够拥有调用终端服务函数以及回调函数的能力,但是这一步还没有将其指向我们自己的中断服务函数。
XUartPs_SetHandler()函数才是真正的设置了我们的中断服务函数。XUartPs_SetInterruptMask()函数设置中断掩码,即哪些中断有效,这里我们设置了XUARTPS_IXR_RXOVR和XUARTPS_IXR_TOUT,分别代表FIFO达到阈值产生中断以及超时产生中断,其它的掩码也可以在xuartps_hw.h文件中找到宏定义。最后XUartPs_EnableUart()函数将UART使能,XScuGic_Enable()函数将中断控制器使能。
//***************************************
// Set serial port working parameters and interrupt service functions
//***************************************
int UartISR_init(XUartPs *InstancePtrUart, XScuGic *InstancePtrGic, u8 INTID)
{
// Set BTUart Params
XUartPs_SetBaudRate(InstancePtrUart, BAUDSETVALIE);
XUartPs_SetOperMode(InstancePtrUart, XUARTPS_OPER_MODE_NORMAL);
XUartPs_SetRecvTimeout(InstancePtrUart, 29);
XUartPs_SetFifoThreshold(InstancePtrUart, 50);
XUartPs_Recv(InstancePtrUart, BtRecvBuffer, BT_MAX_SIZE);
// Enable Interrupt
XScuGic_SetPriorityTriggerType(InstancePtrGic,
INTID, PRIORITY1, TRIG_HIGH_LEVEL);
XScuGic_Connect(InstancePtrGic, INTID,
(Xil_InterruptHandler)XUartPs_InterruptHandler,
(void *)InstancePtrUart);
XUartPs_SetHandler(InstancePtrUart,
(XUartPs_Handler)UartISR_handle, InstancePtrUart);
XUartPs_SetInterruptMask(InstancePtrUart, XUARTPS_IXR_RXOVR | XUARTPS_IXR_TOUT);
XUartPs_EnableUart(InstancePtrUart);
return XST_SUCCESS;
}
中断掩码的宏定义:
#define XUARTPS_IXR_RBRK 0x00002000U /**< Rx FIFO break detect interrupt */
#define XUARTPS_IXR_TOVR 0x00001000U /**< Tx FIFO Overflow interrupt */
#define XUARTPS_IXR_TNFUL 0x00000800U /**< Tx FIFO Nearly Full interrupt */
#define XUARTPS_IXR_TTRIG 0x00000400U /**< Tx Trig interrupt */
#define XUARTPS_IXR_DMS 0x00000200U /**< Modem status change interrupt */
#define XUARTPS_IXR_TOUT 0x00000100U /**< Timeout error interrupt */
#define XUARTPS_IXR_PARITY 0x00000080U /**< Parity error interrupt */
#define XUARTPS_IXR_FRAMING 0x00000040U /**< Framing error interrupt */
#define XUARTPS_IXR_OVER 0x00000020U /**< Overrun error interrupt */
#define XUARTPS_IXR_TXFULL 0x00000010U /**< TX FIFO full interrupt. */
#define XUARTPS_IXR_TXEMPTY 0x00000008U /**< TX FIFO empty interrupt. */
#define XUARTPS_IXR_RXFULL 0x00000004U /**< RX FIFO full interrupt. */
#define XUARTPS_IXR_RXEMPTY 0x00000002U /**< RX FIFO empty interrupt. */
#define XUARTPS_IXR_RXOVR 0x00000001U /**< RX FIFO trigger interrupt. */
#define XUARTPS_IXR_MASK 0x00003FFFU /**< Valid bit mask */
关于XUartPs_Recv()函数
为何初始化UART中断的时候配置完UART以后要先receive一下?什么时候需要receive呢?
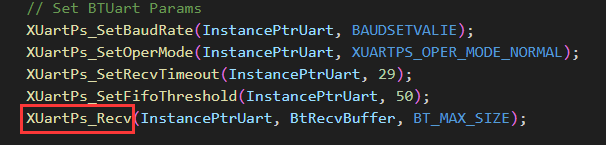
我们先来看一下XUartPs_Recv()函数的源码:
u32 XUartPs_Recv(XUartPs *InstancePtr,
u8 *BufferPtr, u32 NumBytes)
{
u32 ReceivedCount;
u32 ImrRegister;
/* Assert validates the input arguments */
Xil_AssertNonvoid(InstancePtr != NULL);
Xil_AssertNonvoid(BufferPtr != NULL);
Xil_AssertNonvoid(InstancePtr->IsReady == XIL_COMPONENT_IS_READY);
/*
* Disable all the interrupts.
* This stops a previous operation that may be interrupt driven
*/
ImrRegister = XUartPs_ReadReg(InstancePtr->Config.BaseAddress,
XUARTPS_IMR_OFFSET);
XUartPs_WriteReg(InstancePtr->Config.BaseAddress, XUARTPS_IDR_OFFSET,
XUARTPS_IXR_MASK);
/* Setup the buffer parameters */
InstancePtr->ReceiveBuffer.RequestedBytes = NumBytes;
InstancePtr->ReceiveBuffer.RemainingBytes = NumBytes;
InstancePtr->ReceiveBuffer.NextBytePtr = BufferPtr;
/* Receive the data from the device */
ReceivedCount = XUartPs_ReceiveBuffer(InstancePtr);
/* Restore the interrupt state */
XUartPs_WriteReg(InstancePtr->Config.BaseAddress, XUARTPS_IER_OFFSET,
ImrRegister);
return ReceivedCount;
}
我们关注的重点在/* Setup the buffer parameters */部分,可以看到ReceiveBuffer中有三个参数RequestedBytes和RemainingBytes和NextBytePtr。函数将NumBytes也就是我们之前定义的最大字节数赋值给了请求字节数和剩余字节数,将缓冲区首地址赋值给了下一字节的指针。这一步可以当作是一个初始化的步骤,因为在后续的步骤中是要用到这三个参数的,后面也会讲到,以及很重要的一个函数XUartPs_ReceiveBuffer()也会在后面讲到。这就是为什么在配置完了UART后要先receive一下,因为需要初始化三个参数。
关于XScuGic_Connect()函数
前面我们讲到说这个函数的作用是将我们要设置的中断与中断服务函数还有回调函数连接起来,使之能够拥有调用终端服务函数以及回调函数的能力,但是这一步还没有将其指向我们自己的中断服务函数。这句话可以当作是帮助我们理解的部分,但是其实它并不是单纯的这么简单。
这个函数其实确实将我们的中断指向了XUartPs_InterruptHandler()函数,我们来看看这个函数的源码:
void XUartPs_InterruptHandler(XUartPs *InstancePtr)
{
u32 IsrStatus;
Xil_AssertVoid(InstancePtr != NULL);
Xil_AssertVoid(InstancePtr->IsReady == XIL_COMPONENT_IS_READY);
/*
* Read the interrupt ID register to determine which
* interrupt is active
*/
IsrStatus = XUartPs_ReadReg(InstancePtr->Config.BaseAddress,
XUARTPS_IMR_OFFSET);
IsrStatus &= XUartPs_ReadReg(InstancePtr->Config.BaseAddress,
XUARTPS_ISR_OFFSET);
/* Dispatch an appropriate handler. */
if((IsrStatus & ((u32)XUARTPS_IXR_RXOVR | (u32)XUARTPS_IXR_RXEMPTY |
(u32)XUARTPS_IXR_RXFULL)) != (u32)0) {
/* Received data interrupt */
ReceiveDataHandler(InstancePtr);
}
if((IsrStatus & ((u32)XUARTPS_IXR_TXEMPTY | (u32)XUARTPS_IXR_TXFULL))
!= (u32)0) {
/* Transmit data interrupt */
SendDataHandler(InstancePtr, IsrStatus);
}
/* XUARTPS_IXR_RBRK is applicable only for Zynq Ultrascale+ MP */
if ((IsrStatus & ((u32)XUARTPS_IXR_OVER | (u32)XUARTPS_IXR_FRAMING |
(u32)XUARTPS_IXR_PARITY | (u32)XUARTPS_IXR_RBRK)) != (u32)0) {
/* Received Error Status interrupt */
ReceiveErrorHandler(InstancePtr, IsrStatus);
}
if((IsrStatus & ((u32)XUARTPS_IXR_TOUT)) != (u32)0) {
/* Received Timeout interrupt */
ReceiveTimeoutHandler(InstancePtr);
}
if((IsrStatus & ((u32)XUARTPS_IXR_DMS)) != (u32)0) {
/* Modem status interrupt */
ModemHandler(InstancePtr);
}
/* Clear the interrupt status. */
XUartPs_WriteReg(InstancePtr->Config.BaseAddress, XUARTPS_ISR_OFFSET,
IsrStatus);
}
这段代码的核心是中间的一长串判断语句,至于最开始的读寄存器操作,可以在ug585中找到相关的寄存器代表的含义来理解。看中间的判断语句,第一个判断中包含了我们之前设置的中断掩码XUARTPS_IXR_RXOVR,它代表着FIFO达到阈值产生中断,如果判断为该类型的中断则会进入ReceiveDataHandler()函数,源码如下:
static void ReceiveDataHandler(XUartPs *InstancePtr)
{
/*
* If there are bytes still to be received in the specified buffer
* go ahead and receive them. Removing bytes from the RX FIFO will
* clear the interrupt.
*/
if (InstancePtr->ReceiveBuffer.RemainingBytes != (u32)0) {
(void)XUartPs_ReceiveBuffer(InstancePtr);
}
/* If the last byte of a message was received then call the application
* handler, this code should not use an else from the previous check of
* the number of bytes to receive because the call to receive the buffer
* updates the bytes ramained
*/
if (InstancePtr->ReceiveBuffer.RemainingBytes == (u32)0) {
InstancePtr->Handler(InstancePtr->CallBackRef,
XUARTPS_EVENT_RECV_DATA,
(InstancePtr->ReceiveBuffer.RequestedBytes -
InstancePtr->ReceiveBuffer.RemainingBytes));
}
}
这个函数意思就是当接收寄存器剩余字节数不为0时则进入XUartPs_ReceiveBuffer()函数,如果是0则设置Event为XUARTPS_EVENT_RECV_DATA, EventData为(InstancePtr->ReceiveBuffer.RequestedBytes - InstancePtr->ReceiveBuffer.RemainingBytes)也就是接收的字节数,这里调用的才是我们的UartISR_handle()函数,并且函数会进入Event == XUARTPS_EVENT_RECV_DATA判断分支中来,因此我们可以看到,只有缓冲区满了的时候我们的中断服务函数才会进入XUARTPS_EVENT_RECV_DATA.
我们再回到剩余字节数不为0时,函数会进入XUartPs_ReceiveBuffer(),我们来看这个函数的源码:
u32 XUartPs_ReceiveBuffer(XUartPs *InstancePtr)
{
u32 CsrRegister;
u32 ReceivedCount = 0U;
u32 ByteStatusValue, EventData;
u32 Event;
/*
* Read the Channel Status Register to determine if there is any data in
* the RX FIFO
*/
CsrRegister = XUartPs_ReadReg(InstancePtr->Config.BaseAddress,
XUARTPS_SR_OFFSET);
/*
* Loop until there is no more data in RX FIFO or the specified
* number of bytes has been received
*/
while((ReceivedCount < InstancePtr->ReceiveBuffer.RemainingBytes)&&
(((CsrRegister & XUARTPS_SR_RXEMPTY) == (u32)0))){
if (InstancePtr->is_rxbs_error) {
ByteStatusValue = XUartPs_ReadReg(
InstancePtr->Config.BaseAddress,
XUARTPS_RXBS_OFFSET);
if((ByteStatusValue & XUARTPS_RXBS_MASK)!= (u32)0) {
EventData = ByteStatusValue;
Event = XUARTPS_EVENT_PARE_FRAME_BRKE;
/*
* Call the application handler to indicate that there is a receive
* error or a break interrupt, if the application cares about the
* error it call a function to get the last errors.
*/
InstancePtr->Handler(InstancePtr->CallBackRef,
Event, EventData);
}
}
InstancePtr->ReceiveBuffer.NextBytePtr[ReceivedCount] =
XUartPs_ReadReg(InstancePtr->Config.
BaseAddress,
XUARTPS_FIFO_OFFSET);
ReceivedCount++;
CsrRegister = XUartPs_ReadReg(InstancePtr->Config.BaseAddress,
XUARTPS_SR_OFFSET);
}
InstancePtr->is_rxbs_error = 0;
/*
* Update the receive buffer to reflect the number of bytes just
* received
*/
if(InstancePtr->ReceiveBuffer.NextBytePtr != NULL){
InstancePtr->ReceiveBuffer.NextBytePtr += ReceivedCount;
}
InstancePtr->ReceiveBuffer.RemainingBytes -= ReceivedCount;
return ReceivedCount;
}
这段代码的核心在while循环中,循环条件是接收字节数少于缓冲区剩余字节数也就是缓冲区未满并且Rx FIFO非空,其中ReceivedCount指的是本次循环中接收的字节数,会从0开始计数,XUARTPS_SR_RXEMPTY是Rx FIFO空状态寄存器,当为0的时候Rx FIFO不为空,当为1的时候Rx FIFO为空(查阅ug585)。这个循环主要完成的工作是将Rx FIFO中的数取出来放入接收缓冲区中,当缓冲区满了或者Rx FIFO空了的时候,结束循环,进入后续操作。
- 将缓冲区的下一字节的地址加上本次接收字节数;
- 将缓冲区剩余字节数减少本次接收字节数;
- 返回本次接收字节数。
之后程序退回到XUartPs_InterruptHandler()函数中,继续判断,程序在产生FIFO阈值中断的同时也会产生超时中断,因此还会进入ReceiveTimeoutHandler()函数中,(这里有些小问题,具体参考XiLinx SDK FreeRTOS学习记录(五)——串口问题解决全过程以及串口接收中断函数的测试)源码如下:
static void ReceiveTimeoutHandler(XUartPs *InstancePtr)
{
u32 Event;
/*
* If there are bytes still to be received in the specified buffer
* go ahead and receive them. Removing bytes from the RX FIFO will
* clear the interrupt.
*/
if (InstancePtr->ReceiveBuffer.RemainingBytes != (u32)0) {
(void)XUartPs_ReceiveBuffer(InstancePtr);
}
/*
* If there are no more bytes to receive then indicate that this is
* not a receive timeout but the end of the buffer reached, a timeout
* normally occurs if # of bytes is not divisible by FIFO threshold,
* don't rely on previous test of remaining bytes since receive
* function updates it
*/
if (InstancePtr->ReceiveBuffer.RemainingBytes != (u32)0) {
Event = XUARTPS_EVENT_RECV_TOUT;
} else {
Event = XUARTPS_EVENT_RECV_DATA;
}
/*
* Call the application handler to indicate that there is a receive
* timeout or data event
*/
InstancePtr->Handler(InstancePtr->CallBackRef, Event,
InstancePtr->ReceiveBuffer.RequestedBytes -
InstancePtr->ReceiveBuffer.RemainingBytes);
}
函数先判断缓冲区剩余字节数是否为0,若不为0则会进入XUartPs_ReceiveBuffer()函数,上面已经介绍过这个函数的作用。若是程序从ReceiveDataHandler()函数中退出又进入XUartPs_ReceiveBuffer()函数,要么Rx FIFO为空,要么缓冲区已满,此时要么不会进入XUartPs_ReceiveBuffer()函数,要么进去了也不会进行任何操作。完成接收函数之后再次判断剩余字节数是否为0,若缓冲区剩余字节不为0,将Event赋值为XUARTPS_EVENT_RECV_TOUT,若缓冲区已满,则将其赋值为XUARTPS_EVENT_RECV_DATA,这里也能看出只有当接收缓冲区满的时候才会进入XUARTPS_EVENT_RECV_DATA分支,否则进入XUARTPS_EVENT_RECV_TOUT分支。然后进入我们自己的中断服务函数进行后续操作。
至此,UART串口通信的C语言代码就全部学完了。